Estimation of the beam ion confinement time in LHD
The confinement time of fast ions, which are generated by the neutral beam injection, has been estimated quantitatively in the LHD deuterium experiment by using neutron measurement and the integrated simulation. This estimation is the first achievement in large size helical systems, to our knowledge. This research can reduce ambiguities from the plasma heating profile and can contribute to the clarification of the physics phenomena in the LHD.
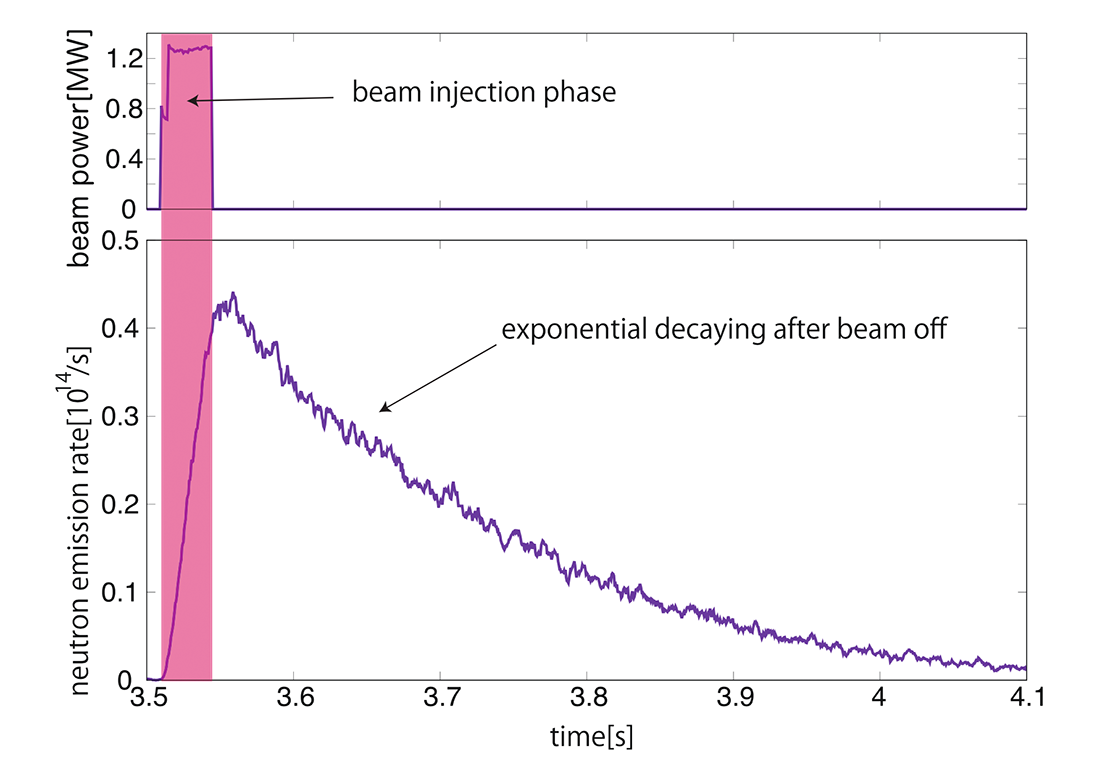
The confinement time of fast ions, which are generated by the neutral beam injection, has been estimated quantitatively in the LHD deuterium experiment by using neutron measurement and integrated simulation. This estimation is the first achievement in large size helical systems, to our knowledge. This research can reduce ambiguities from the plasma heating profile and can contribute to the clarification of the physics phenomena in the LHD.
Fusion plasmas require plasma heating to sustain the plasma temperature. Neutral beam injection (NBI), which injects energetic particles into plasmas, is one of the heating methods. The plasma heating efficiency is sensitive to the confinement time of the energetic particle propelled by NBI. In this research we have achieved an estimation of the confinement time of energetic particles in the LHD by using neutron measurement and integrated simulation.
Besides, we have clarified that we can analyze the impurity ion ratio in plasmas from the comparison between the simulation result, using the obtained confinement time, and the experimental result. In general, it is difficult to measure the impurity ion ratio directly. Therefore, this is estimated by a combination of several measurements. Owing to the result of this paper, neutron measurement can also contribute to the estimation of the impurity ion ratio.
The confinement time and the impurity ion ratio, which are estimated by this paper, can contribute to the analyses of LHD experimental data.
This research result was published on June 17, 2020 in Journal of Plasma Physics, a journal on plasma physics by Cambridge University Press.
