Energetic ion charge exchange spectroscopy using higher energy beam
We have successfully made Fast Ion D-Alpha (FIDA) measurements using a high energy neutral beam in a deuterium plasma experiment in the Large Helical Device (LHD). FIDA measurements have been done with relatively low energy neutral beams. This result shows that the measurements can be accomplished with high energy neutral beams, which are used in conditions similar to those in fusion reactors such as ITER and JT-60SA.
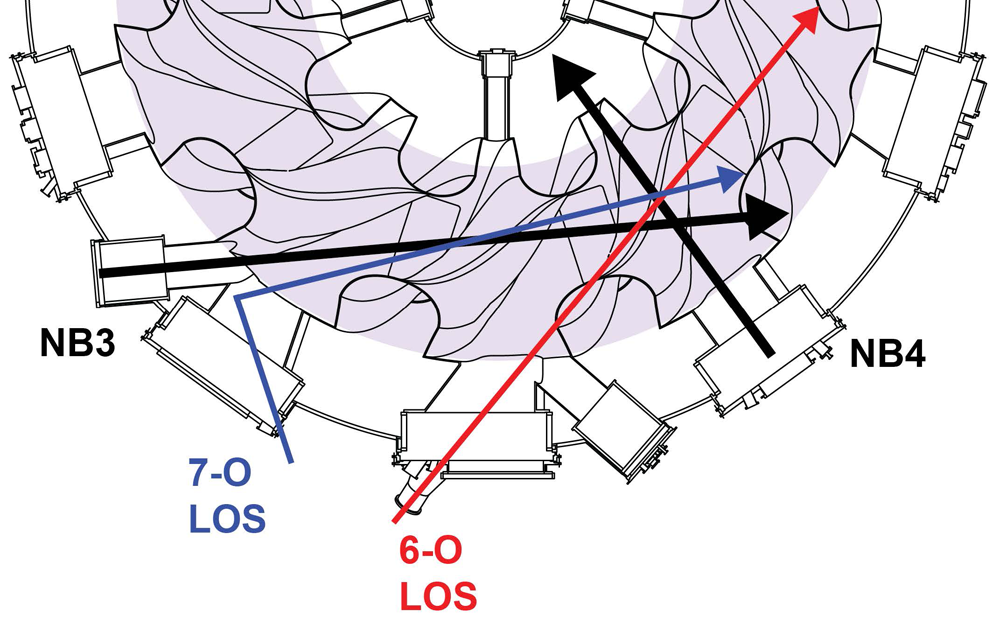
Future nuclear burning plasmas will be heated by energetic alpha particles generated by the fusion reaction between deuterium and tritium. Therefore, good confinement of energetic ions is essential. Fast ion charge exchange (FIDA) is used in magnetic confinement devices around the world to measure the distribution of energetic ions confined in a magnetic field by using a neutral beam. This exchanges the charge of energetic ions, confined in a magnetic cage, and enables observation of the emission from the charge-exchanged energetic particles. FIDA is used in magnetic confinement devices around the world and its measurements have been achieved using positive ion source neutral beams with relatively low energy. However, future experimental devices close to fusion reactors will mainly use negative ion source neutral beams with relatively high energy for heating and control. Also, it has not been experimentally demonstrated whether FIDA measurements are possible with high energy neutral beams.
The research team concentrated on a high-energy neutral beam installed in the LHD, utilizing it for the FIDA measurements. In the past, when the angle between the negative ion source neutral beam and the FIDA measurement line of sight was relatively large, it was difficult to do FIDA measurements. This was due to the high noise level of the signal. By setting up a new line of sight with this angle as small as possible, we succeeded in measuring Doppler-shifted luminescence, thought to be caused by charge exchange of high energy ions. The measured emission spectrum was qualitatively consistent with that predicted by FIDASIM, a numerical simulation code developed mainly in the US, indicating that these emissions were due to the charge exchange of energetic ions. This result experimentally demonstrated the feasibility of observing energetic ions using a high energy negative ion source neutral beam.
This work was conducted by Masaki Osakabe and his research group at the National Institute for Fusion Science, in collaboration with W.H.J. Hayashi, Ph.D. student, Prof. W.W. Heidbrink at the University of California, Irvine, US, Dr. C.M. Muscatello and Dr. D.J. Lin at General Atomics, US.
The results of this research were selected for a poster presentation at the 29th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference in 2023 and published in the Journal of Instrumentation, an international publication on metrology, dated December 6, 2024.
